Math Notes
:: Notes / Resources :: Notes
Page 1 of 1
 Math Notes
Math Notes
June 16 2010
1st Quarter - Advanced Algebra
2nd and 3rd Quarter - Trigonometry
4th Quarter - Statistics
June 17 2010
Language, Notation and Numbers in Mathematics
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Notation
{} - braces, denotes set
… - ellipses, denotes pattern of continuous indefinitely
∈ - denotes element
⊆ - denotes subset
⊂ - denotes proper subset
∅ - null set or empty braces
, - to separate elements of the set
June 18 2010
Definitions:
Reading Notations:
Q={p/q|p, q ∈ Z;q≠0}
............⇓
Q is set of p over q such that p and q element of integers where q is not equal to zero
*| - such that
*; - where
1st Quarter - Advanced Algebra
2nd and 3rd Quarter - Trigonometry
4th Quarter - Statistics
June 17 2010
Language, Notation and Numbers in Mathematics
- Natural Numbers - most basic numbers, denoted by N
ex. {1,2,3,...} - Whole Numbers - natural numbers with zero(0), denoted by W
ex. {0,1,2,3,...} - Integers - denoted by Z
A. Positive - greater than zero
ex. {1,2,3,...}
B. Negative - less than zero
ex. {-1,-2,-3,...} - Rational Numbers - fractions and mixed numbers, denoted by Q
ex. {1 1/2,3/5,2/3,...} - Irrational Numbers - denoted by H
- Real Numbers - all rational and irrational, denoted by R
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1Notation
{} - braces, denotes set
… - ellipses, denotes pattern of continuous indefinitely
∈ - denotes element
⊆ - denotes subset
⊂ - denotes proper subset
∅ - null set or empty braces
, - to separate elements of the set
June 18 2010
Definitions:
- algebraic term - collection of factors that may include numbers, variables or expressions within parentheses
- constant - a term that consists of non-variable number
- variable - a symbol, commonly a letter, used to represent unknown quantity
- coefficient - constant factor of a term
- algebraic expression - a single term or a sum or difference of terms
*Proper subset - all the elements of a set
Reading Notations:
Q={p/q|p, q ∈ Z;q≠0}
............⇓
Q is set of p over q such that p and q element of integers where q is not equal to zero
*| - such that
*; - where
Last edited by belly on Thu Jul 01, 2010 9:39 pm; edited 1 time in total
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
June 21 2010
Relations - a correspondence between two sets
.............- can be represented using (A) Mapping Notation, (B) Bar Graph, (C) Ordered Pair, ...............and (D) Rectangular Coordinate System or Cartesian Plane
June 22 2010
Function - a relation that pairs each element from the domain with exactly one element from the range
Ex. Determine whether a relation is a function.
Finding the value of function f(x) = 2x2-3x
Relations - a correspondence between two sets
.............- can be represented using (A) Mapping Notation, (B) Bar Graph, (C) Ordered Pair, ...............and (D) Rectangular Coordinate System or Cartesian Plane
- A. Mapping Notation
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2B. Bar Graph
 Fig. 3
Fig. 3*
 - denotes zero-n, used when it does not start from zero(ex. years)
- denotes zero-n, used when it does not start from zero(ex. years)*x - independent
_y - dependent
C. Ordered Pairs
__..(2008, 50) (2009, 100) (2010, 150) (2011, 225)
D. Cartesian Plane or Rectangular Coordinate System
__..-used in the same way
June 22 2010
Function - a relation that pairs each element from the domain with exactly one element from the range
Ex. Determine whether a relation is a function.
- A.
...
 Fig. 4
Fig. 4B.
...
 Fig. 5
Fig. 5..................FUNCTION
C. (1,2) (2,3) (3,4) (4,5)
.......X........Y
.......1........2
.......2........3
.......3........4
.......4........5
.....FUNCTION
D.
...
 Fig. 6.1
Fig. 6.1...*Vertical Line Test - a graph is a function if and only if every vertical line intersects
...the graph at most one point
...
 Fig. 6.2
Fig. 6.2Finding the value of function f(x) = 2x2-3x
- ƒ(3) = 2(3)2-3(3)
ƒ(3) = 18-9
ƒ(3) = 9 - ƒ(-2) = 2(-2)2-3(-2)
*f(-2) ≠ ƒ•(-2)
ƒ(-2) = 14 - ƒ(-x) = 2(x)2-2(-x)
ƒ(-x) = 2x2+3x - ƒ(x+1) = 2(x+1)2-3(x-1)
ƒ(x+1) = 2(x2+2x+1)-3x-3_____*special product
ƒ(x+1) = 2x2+x-1
Last edited by belly on Thu Jul 01, 2010 9:41 pm; edited 2 times in total
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
June 23 2010
Domain of Function - largest set of all real numbers for which the value of f(x) is a real number
*Don't mind the extra blue text. There was a glitch so I had to change the color. There's nothing that special about it.
Domain of Function - largest set of all real numbers for which the value of f(x) is a real number
- Ex. A. ƒ(m) = 3(m)+2
... Df = R or m ∈ (-∞,∞) or m = {m|m ∈ R}
Ex. B. ƒ(x) = 3/x+4
... Df = R-{4} or x ∈ (∞,-4) ∪(-4,∞) or x = {x|x≠4}
Ex. C. ƒ(x) = √2x+3
...Note: 2x+3 ≥ 0
.......... 2x ≥ -3
.......... x ≥ -3/2
... Df = {x|x ≥ -3/2} or x ∈ [-3/2,∞)
Ex. D ƒ(x) = √4+3x
...Note: 4+3x ≥ 0
.......... 3x ≥ -4
.......... x ≥ -4/3
... Df = {x|x ≥ -4/3} or x ∈ [-4/3, ∞)
Ex. E ƒ(x) = 3x2+5
... Df = R
Ex. F ƒ(x) = 3/5+x
... Df = R - {5}
*Don't mind the extra blue text. There was a glitch so I had to change the color. There's nothing that special about it.
Last edited by belly on Sun Jun 27, 2010 1:40 pm; edited 2 times in total
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
June 24 2010
Operations of Function
ƒ(x) = 3x+4..........g(x) = 2x-3
Operations of Function
ƒ(x) = 3x+4..........g(x) = 2x-3
- The sum of ƒ+g is the function defined by ƒ(x)+g(x)
...(ƒ+g)(x) = ƒ(x)+g(x)
_________ = (3x+4)+(2x-3)
_________ = 5x+1
Df+g = R - The difference of ƒ-g is the function defined by ƒ(x)-g(x)
...(ƒ-g)(x)=ƒ(x)
________ = (3x+4)-(2x-3)
________ = x+7
Dƒ-g = R - The product of ƒ•g is the function defined by ƒ(x)•g(x)
...(ƒ•g)(x) = ƒ(x)•g(x)
___._____ = (3x+4)•(2x-3)
_____.___ = 6x2-9x+8x-12
______.__ = 6x2-x-12
Dƒ•g = R - The quotient of ƒ/g is the function defined by ƒ(x)/g(x)
...(ƒ/g)(x) = ƒ(x)/g(x)
_________= 3x+4/2x-3
Dƒ/g = R-{3/2}
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
June 29 2010
Analyzing Graph of Function
...A. Even/Odd
.......Even Function (p. 207)
..........-a function ƒ is an even function if and only if for each point (x,y) on
............the graph of ƒ, the point (-x,y) is also on the graph
..........Function Notation: ƒ(-x)=ƒ(x)
*Mirror image with respect to the y-axis.
Ex.
 Fig. 7
Fig. 7
Ex. Even function, continue.
 Fig. 8.1
Fig. 8.1
________________________⇓
 Fig. 8.2
Fig. 8.2
Note: When folding, fold on y-axis.
.......Odd Function
..........-a function is an odd function if and only if for each (x,y) on the graph of ƒ the point (-x,-y) is also on the graph
Ex.
 Fig. 9
Fig. 9
 Fig. 10
Fig. 10
*Mirror image with respect to the point of origin.
Note: When folding, -x-axis on +y-axis.
*
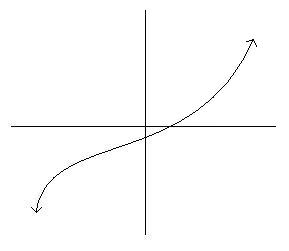 Fig. 11
Fig. 11
____________NEITHER
It does not lie on the point of origin and is not a mirror image with respect to the y-axis.
...B. Increasing/Decreasing
.......Given and interval (I) that is a subset of the domain with x1 and x2 in I and x2>x1
.......Ex. [-3,0] x1:-3 x2:0
.......*a function is increasing at I if ƒ(x2)>ƒx1 for all x1 and x2 in I
.......*a function is decreasing at I if ƒ(x2)<ƒ(x1) for all x1 and x2 in I
.......*a function is constant at I if ƒ(x2) = ƒ(x1) for all x1 and x2 in I
Ex. Given:
I: [0,∞)
 Fig. 12
Fig. 12
...x...|..ƒ(x)/y
x1: 1 | __1
x2: 2 | __4
4>1 so the given function is INCREASING at the given interval
*ƒ(s):y axis and s:x axis no matter what letter is used.
Analyzing Graph of Function
...A. Even/Odd
.......Even Function (p. 207)
..........-a function ƒ is an even function if and only if for each point (x,y) on
............the graph of ƒ, the point (-x,y) is also on the graph
..........Function Notation: ƒ(-x)=ƒ(x)
*Mirror image with respect to the y-axis.
Ex.
 Fig. 7
Fig. 7Ex. Even function, continue.
 Fig. 8.1
Fig. 8.1________________________⇓
 Fig. 8.2
Fig. 8.2Note: When folding, fold on y-axis.
.......Odd Function
..........-a function is an odd function if and only if for each (x,y) on the graph of ƒ the point (-x,-y) is also on the graph
Ex.
 Fig. 9
Fig. 9 Fig. 10
Fig. 10*Mirror image with respect to the point of origin.
Note: When folding, -x-axis on +y-axis.
*
 Fig. 11
Fig. 11____________NEITHER
It does not lie on the point of origin and is not a mirror image with respect to the y-axis.
...B. Increasing/Decreasing
.......Given and interval (I) that is a subset of the domain with x1 and x2 in I and x2>x1
.......Ex. [-3,0] x1:-3 x2:0
.......*a function is increasing at I if ƒ(x2)>ƒx1 for all x1 and x2 in I
.......*a function is decreasing at I if ƒ(x2)<ƒ(x1) for all x1 and x2 in I
.......*a function is constant at I if ƒ(x2) = ƒ(x1) for all x1 and x2 in I
Ex. Given:
I: [0,∞)
 Fig. 12
Fig. 12...x...|..ƒ(x)/y
x1: 1 | __1
x2: 2 | __4
4>1 so the given function is INCREASING at the given interval
*ƒ(s):y axis and s:x axis no matter what letter is used.
Last edited by belly on Mon Jul 05, 2010 7:59 pm; edited 1 time in total
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
July 1 2010
Given: I: (-∞,0]
_____ Fig. 12
....x....|..ƒ(x)/y
x1: -2 | __4
x2: -1 | __1
ƒ(x2)<ƒ(x1) so the function at the given interval is DECREASING
Note: If from left to right the graph goes down, it is decreasing.
____. If from left to right the graph goes up, it is increasing.
Given: I: (-∞,∞)
 Fig. 13
Fig. 13
The function CANNOT BE DETERMINED at the given I.
*Look at graph, use I to know which certain part to look at.
...C. Maximum and Minimum
.......Global maximum-absolute maximum
________________..-names the largest range value over the entire domain
.......Local maximum-relative maximum
________________.-names the largest range value over the specified interval
.......Global minimum-names the smallest range value over the entire domain
.......Local minimum-names the smallest range value over the specified interval
Ex.
 Fig. 14
Fig. 14
Dƒ: [-7,6]
Rƒ: [0,10]
Global Maximum: (0,10)
Global Minima: (6,0) and (-7,0)
Ex.
 Fig. 15
Fig. 15
Dƒ: R (because of arrows)
Rƒ: [0,∞)
Global Maximum: N/A (infinity)
Global Minimum: (0,0)
Given: I: (-∞,0]
_____ Fig. 12
....x....|..ƒ(x)/y
x1: -2 | __4
x2: -1 | __1
ƒ(x2)<ƒ(x1) so the function at the given interval is DECREASING
Note: If from left to right the graph goes down, it is decreasing.
____. If from left to right the graph goes up, it is increasing.
Given: I: (-∞,∞)
 Fig. 13
Fig. 13The function CANNOT BE DETERMINED at the given I.
*Look at graph, use I to know which certain part to look at.
...C. Maximum and Minimum
.......Global maximum-absolute maximum
________________..-names the largest range value over the entire domain
.......Local maximum-relative maximum
________________.-names the largest range value over the specified interval
.......Global minimum-names the smallest range value over the entire domain
.......Local minimum-names the smallest range value over the specified interval
Ex.
 Fig. 14
Fig. 14Dƒ: [-7,6]
Rƒ: [0,10]
Global Maximum: (0,10)
Global Minima: (6,0) and (-7,0)
Ex.
 Fig. 15
Fig. 15Dƒ: R (because of arrows)
Rƒ: [0,∞)
Global Maximum: N/A (infinity)
Global Minimum: (0,0)
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
July 7 2010
Composition of Function
Given two functions ƒ and g, the composition of ƒ with g is defined by (ƒog)(x) = ƒ[g(x)]
Ex. ƒ(x) = 3x+1
___g(x) = 2x
_____ 1. (ƒog)(x) = 3(2x)+1
_______________.= 3(g(x))+1
_______________.= 6x+1
_____ 2. (goƒ)(x) = 2(f(x))
_______________ = 2(3x+1)
_______________ = 6x+2
Ex. ƒ(x) = 2x+x
___g(x) = x+1
_____ 1. (ƒog)(x) = 2(g(x))+(g(x))
_______________ = 2(x+1)+(x+1)
_______________ = 2x+2+x+1
_______________ = 3x+3
_____ 2. (goƒ)(x) = (ƒ(x))+1
_______________ = 2x+x+1
_______________ = 3x+1
June 12 2010
Linear and Quadratic Functions
(p.74, 206 and 294)
General Linear Equation
Ax+B = 0
Standard Linear Equation
Ax+By = C
Forms and Formulas for Linear Equation
Composition of Function
Given two functions ƒ and g, the composition of ƒ with g is defined by (ƒog)(x) = ƒ[g(x)]
Ex. ƒ(x) = 3x+1
___g(x) = 2x
_____ 1. (ƒog)(x) = 3(2x)+1
_______________.= 3(g(x))+1
_______________.= 6x+1
_____ 2. (goƒ)(x) = 2(f(x))
_______________ = 2(3x+1)
_______________ = 6x+2
Ex. ƒ(x) = 2x+x
___g(x) = x+1
_____ 1. (ƒog)(x) = 2(g(x))+(g(x))
_______________ = 2(x+1)+(x+1)
_______________ = 2x+2+x+1
_______________ = 3x+3
_____ 2. (goƒ)(x) = (ƒ(x))+1
_______________ = 2x+x+1
_______________ = 3x+1
June 12 2010
Linear and Quadratic Functions
(p.74, 206 and 294)
General Linear Equation
Ax+B = 0
Standard Linear Equation
Ax+By = C
Forms and Formulas for Linear Equation
- Slope Formula
y = mx+b
m:slope
b:y-intercept
Ex. Write the standard form of the equation of each line.
__y = -7/5x+1
__5(y+7/5x) = (1)(5)
__7x+5y = 5
___x_|_y_
___0_|_1
__5/7.|_0
__7(0)+5y = 5
__5y/5=5/5
__y = 1
__7x+5(0) = 5
__7x/7= 5/7
__x = 5/7
Ex. y = 3/2x+5
__2(-3/2x+y) = (5)(2)
__-3x+2y = 10
_____x_|_y_
_____0_|_5
__10/-3.|.0
__-3(0)+2y = 10
__2y/2= 10/2
__y = 5
__-3x+2(0) = 10
__-3x/-3= 10/-3
__x = 10/-3
*When the slope is positive, the function is increasing.
*When the slope is negative, the function is decreasing.
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
June 13 2010
Linear Functions
Linear Functions
- B. Point-slope Form
__.y-y1 = m(x-x1)
__.Ex. A. ♥P(0,5) ♦Q(3,2)
__. ♥: y-5 = 5-2/0-3(x-0)
__. y-5 = -1(x-0)
__. ♦: y-2 = -1(x-3)
__. Standard Form
__. ♥: y-5 = -1(x-0)
__. y-5 = -x
__. y+x = 5
__. ♦: y-2 = -1(x-3)
__. y-2 = -x+3
__. y+x = 5
__.Ex. B. ♥ C(3,5) ♦ S(6,8 )
__. ♥: y-5 = 8-5/6-3(x-3)
__. y-5 = 1(x-3)
__. ♦: y-8 = 1(x-6)
__. Standard Form
__. ♥: y-5 = 1(x-3)
__. y-x = 2
__. ♦: y-8 = 1(x-6)
__. y-x = 2
__. x and y intercept
__. y-x = 2
__. y-(0) = 2
__. y = 2
__. (0)-x = 2
__. x = -2
Last edited by belly on Wed Jun 15, 2011 9:50 pm; edited 4 times in total
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
July 19 2010
Quadratic Function and its Application
*A quadratic function is in the form of ƒ(x) = ax2+bx+c
*The domain of quadratic function is all R, Dƒ = {x|x∈R}
*Range is to be solved
a>0 Fig. 16.1
Fig. 16.1
a<0 Fig. 16.2
Fig. 16.2
Ex. A car manufacturer can produce 15 cars per month. The profit made from the sales of these cars is modeled by p(x) = -0.2x2+4x-3. Where p(x) is the profit in hundred thousand dollars per month and x is the number of cars sold. Based on this model.
a. Find the y-intercept and explain what it means
__p(0) = 0+0-3 = -3
__y-intercept: (0,-3)
__They loose 300,000 dollars if they can't sell the cars
b. How many cars should be made and sold to maximize profit.
__Find vertex(x) = -b/2a = 4/0.4
__∴ 10
c. What is the maximum profit?
__p(10) = -0.2(10)2+4(10)-3
__p(10) = 17
__∴ maximum profit = 1,700,000 dollars
July 20 2010
Axis of Symmetry - vertical line passing through the vertex
*Completing the Square(CS) - (b/2)2
*Quadratic Formula - x=-b±√4ac-b2/2a
*The rest are in the problem set.
Quadratic Function and its Application
*A quadratic function is in the form of ƒ(x) = ax2+bx+c
*The domain of quadratic function is all R, Dƒ = {x|x∈R}
*Range is to be solved
a>0
 Fig. 16.1
Fig. 16.1a<0
 Fig. 16.2
Fig. 16.2Ex. A car manufacturer can produce 15 cars per month. The profit made from the sales of these cars is modeled by p(x) = -0.2x2+4x-3. Where p(x) is the profit in hundred thousand dollars per month and x is the number of cars sold. Based on this model.
a. Find the y-intercept and explain what it means
__p(0) = 0+0-3 = -3
__y-intercept: (0,-3)
__They loose 300,000 dollars if they can't sell the cars
b. How many cars should be made and sold to maximize profit.
__Find vertex(x) = -b/2a = 4/0.4
__∴ 10
c. What is the maximum profit?
__p(10) = -0.2(10)2+4(10)-3
__p(10) = 17
__∴ maximum profit = 1,700,000 dollars
July 20 2010
Axis of Symmetry - vertical line passing through the vertex
*Completing the Square(CS) - (b/2)2
*Quadratic Formula - x=-b±√4ac-b2/2a
*The rest are in the problem set.
Last edited by belly on Mon Aug 02, 2010 11:32 pm; edited 4 times in total
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
July 21 2010
Transformation
Basic Quadratic Formula
ƒ(x) = x2 → opens upward
 Fig. 17
Fig. 17
g(x) = (x-1)2 → ƒ(x) = a(x-h)2
h = 1 (→)
k = -2 (↓)
Ex. m(x) = x2+9x+4
a = 1 b = 9 c = 4
h = -9/2(1) = -9/2 = -4.5
k = 4(1)(4)=92/4(1) = 16-81/4 = -65/4 = -16.25
ƒ(x) = -x1 → opens downward
Transformation
Basic Quadratic Formula
ƒ(x) = x2 → opens upward
 Fig. 17
Fig. 17g(x) = (x-1)2 → ƒ(x) = a(x-h)2
h = 1 (→)
k = -2 (↓)
Ex. m(x) = x2+9x+4
a = 1 b = 9 c = 4
h = -9/2(1) = -9/2 = -4.5
k = 4(1)(4)=92/4(1) = 16-81/4 = -65/4 = -16.25
ƒ(x) = -x1 → opens downward
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
June 27 '10
Polynomial Functions
Long Division
A. (k3-k2-k-2)÷k-2

= k2+k+1
B. (-8x4+36x3+14x2+25x+25)÷x-5

= -8x3-4x2-6x-5
C. (r3+2r2-33r+7)÷r+7

= r2 - 5r +2 - 7/ r + 7 or r2 - 5r + 2, R: -7
D. (8v5+324_5v+20)÷v+4

= 8v4 + 5
Synthetic Division
A.
 Fig. 18
Fig. 18
= k2+k+1
*2 is the negative coefficient of the divisor
B.
 Fig 19
Fig 19
= -8x3-4x2-6x-5
C.
 Fig. 20
Fig. 20
= 8v4+5
D.
 Fig. 21
Fig. 21
= r2-5r+2-7/r+7
Factor Theorem
__ For a polynomial P(x)
___ 1. If p(c) = 0, then x-c is a factor of p(x)
___ 2. If x-c is a factor then p(c) = 0
_____A. p(2) = (2)3-(2)2-2-2
___________ = 8-4-2-2
___________ = 0
Remainder Theorem
__If a polynomial p(x) is divided by (x-c) using synthetic division the remainder is equal to p(c)
Polynomial Functions
Long Division
A. (k3-k2-k-2)÷k-2

= k2+k+1
B. (-8x4+36x3+14x2+25x+25)÷x-5

= -8x3-4x2-6x-5
C. (r3+2r2-33r+7)÷r+7

= r2 - 5r +2 - 7/ r + 7 or r2 - 5r + 2, R: -7
D. (8v5+324_5v+20)÷v+4

= 8v4 + 5
Synthetic Division
A.
 Fig. 18
Fig. 18= k2+k+1
*2 is the negative coefficient of the divisor
B.
 Fig 19
Fig 19= -8x3-4x2-6x-5
C.
 Fig. 20
Fig. 20= 8v4+5
D.
 Fig. 21
Fig. 21= r2-5r+2-7/r+7
Factor Theorem
__ For a polynomial P(x)
___ 1. If p(c) = 0, then x-c is a factor of p(x)
___ 2. If x-c is a factor then p(c) = 0
_____A. p(2) = (2)3-(2)2-2-2
___________ = 8-4-2-2
___________ = 0
Remainder Theorem
__If a polynomial p(x) is divided by (x-c) using synthetic division the remainder is equal to p(c)
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
 Math Notes
Math Notes
2nd Quarter
Quarter Outline:
August 23 2010
Review Triangles and Properties of Triangles
Basic Properties
Similar triangles - all corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are proportional
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
b/f=c/e or b/c = f/e
Special Right Triangles
45-45-90
30-60-90
August 24 2010
Angle Measure in Radians
*rotation - one side moves
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2
*associates angles with circles and rectangular coordinate system (Cartesian plane)
 Fig. 3
Fig. 3
Co-terminal angles-angles that share an initial and terminal side
Ex. Fig. 4
Fig. 4
(+) co-terminal --> 360° + 60° = 420°
(-) co-terminal --> -360° + 60° = -300°
Definitions:
Standard Position - position of an angle when the initial side is at positive x-axis
Quadrantal Angle - angle at its standard position and the terminal side coincides with the axes
*All quadrantal angles are central angles
*All angles at standard position are central angles
Quarter Outline:
- Angle Measure, Special Triangles and Angles
- Trigonometry of Right Triangle
- Unit Circle
- Trigonometry of Real Numbers
- Graph of sine, cosine, secant, co-secant, tangent and cotangent
- Fundamental Identities and Families of Identities
- Constructing and Verifying Identities
August 23 2010
Review Triangles and Properties of Triangles
Basic Properties
- The sum of the interior angles is 180°
- The combined length of any two sides exceeds that of the third.
- Larger angles are opposite the larger side.
Similar triangles - all corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are proportional
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1b/f=c/e or b/c = f/e
Special Right Triangles
45-45-90
- The legs are equal
- The hypotenuse is √2 times the length of either leg
30-60-90
- The hypotenuse is 2 times the shorter leg
- The longer leg is √3 times the shorter leg
August 24 2010
Angle Measure in Radians
*rotation - one side moves
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2*associates angles with circles and rectangular coordinate system (Cartesian plane)
 Fig. 3
Fig. 3Co-terminal angles-angles that share an initial and terminal side
Ex.
 Fig. 4
Fig. 4(+) co-terminal --> 360° + 60° = 420°
(-) co-terminal --> -360° + 60° = -300°
Definitions:
Standard Position - position of an angle when the initial side is at positive x-axis
Quadrantal Angle - angle at its standard position and the terminal side coincides with the axes
*All quadrantal angles are central angles
*All angles at standard position are central angles
King Camacho- Posts : 48
Join date : 2009-12-16
:: Notes / Resources :: Notes
Page 1 of 1
Permissions in this forum:
You cannot reply to topics in this forum|
|
|

 Home
Home